Extracorporeal Membrane Oxygenation (ECMO) systems are critical in life-support procedures, providing temporary cardiac and respiratory support for patients with severe heart or lung failure. A key component of these systems is the pump, which circulates blood through the circuit and ensures effective gas exchange. However, the interaction of blood with pump surfaces can lead to thrombosis, hemolysis, and biofouling. This article explores the role of pumps in ECMO systems, highlights the challenges associated with pump-induced thrombosis, and discusses the potential of advanced surface coatings to enhance pump performance and biocompatibility.
ECMO systems provide life-saving support by oxygenating the blood and removing carbon dioxide outside the body, often for extended periods. Central to their operation is the pump, which propels blood through the circuit, ensuring continuous circulation and effective oxygenation.
The nature of blood contact within these mechanical systems presents challenges, including thrombosis, hemolysis, and biofouling. These complications not only compromise the performance of the ECMO system but also pose significant risks to patient safety. Addressing these issues requires innovations in pump design and the application of advanced surface coatings that improve hemocompatibility and minimize blood trauma.
The Role of Pumps in ECMO Systems
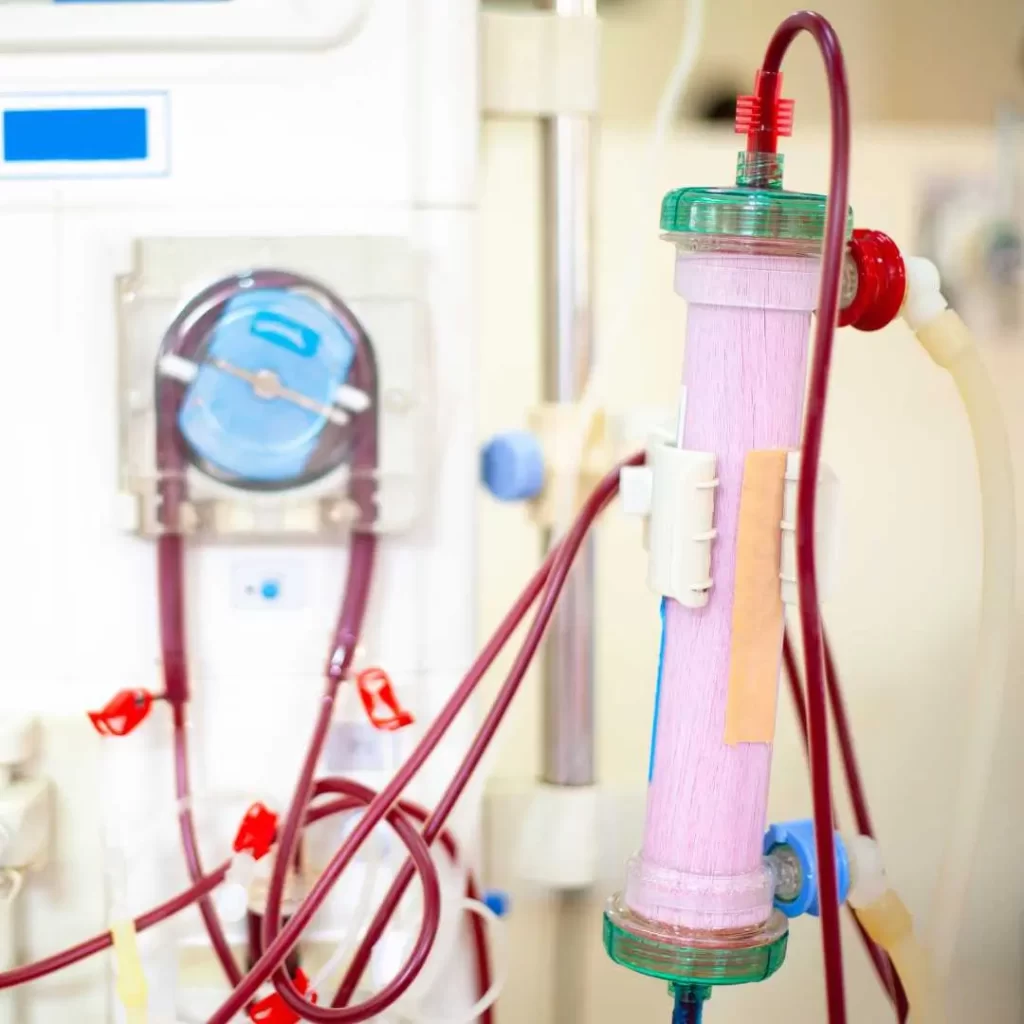
Pumps in ECMO systems are responsible for maintaining the continuous blood flow through the circuit. They ensure blood is drawn from the patient, passes through the oxygenator for gas exchange, and is returned to the body.
The two most commonly used pump types in ECMO systems are:
Centrifugal Pumps: These pumps use a spinning impeller to generate centrifugal force, propelling blood through the circuit. They are widely favored for their gentle handling of blood, reduced hemolysis, and lower thrombosis risk.
Roller Pumps: These create a peristaltic motion by compressing a flexible tube to push blood forward. While reliable and precise in flow control, they are associated with higher risks of hemolysis and tubing wear, which can lead to clot formation.
In addition, other pump types, such as axial pumps, diagonal flow pumps, and pulsatile pumps, are used in specific ECMO configurations or related extracorporeal devices. Each type has its unique advantages and limitations, with centrifugal pumps being the most common in modern ECMO systems due to their balance of efficiency and safety.
Challenges of Pump-Induced Thrombosis
The interaction between blood and pump surfaces can result in several complications:
- Thrombosis: Shear forces within the pump can activate platelets and initiate clot formation, posing risks of embolism or device occlusion.
- Hemolysis: High shear stresses damage red blood cells, releasing free hemoglobin that can lead to oxidative stress and organ damage.
- Energy Losses: Suboptimal flow dynamics within the pump increase energy demands and reduce overall system efficiency.
These challenges necessitate advanced strategies to enhance pump performance and ensure patient safety.
Innovative Coating Technologies for ECMO Pumps
Advanced surface coatings offer a promising solution to mitigate pump-induced complications. These technologies are designed to improve hemocompatibility, reduce shear stress, and minimize protein and microbial adhesion:
- Hydrophilic Coatings: These create a water-attracting layer on pump surfaces, reducing platelet and protein adhesion and promoting smoother blood flow.
- Nitric Oxide (NO)-Releasing Coatings: By mimicking the natural antithrombotic properties of vascular endothelium, NO-releasing coatings prevent platelet activation and aggregation, ensuring thrombus-free operation.
- Endothelialization Promoting Coatings: These coatings replicate the properties of natural endothelial cells, reducing thrombogenicity and supporting long-term hemocompatibility. Smart Reactors’ Camouflage™ technology exemplifies this innovation.
- Zwitterionic Materials: Charge-neutral coatings that resist protein and microbial adhesion, ensuring the longevity and cleanliness of pump surfaces.
These coatings improve the interface between blood and pump surfaces, addressing biological and mechanical challenges while enhancing system performance.
Applications and Benefits
Coated pumps in ECMO systems offer significant advantages, including:
- Reduced Thrombosis Risk: By minimizing platelet adhesion and activation, coatings prevent clot formation and improve pump safety.
- Lower Hemolysis Rates: Coatings that reduce shear stress protect red blood cells, ensuring efficient oxygen transport and reducing complications.
- Enhanced Biocompatibility: Improved blood compatibility reduces inflammatory responses and the need for systemic anticoagulation.
- Increased Device Longevity: Antimicrobial and non-fouling coatings maintain pump functionality and reduce maintenance requirements.
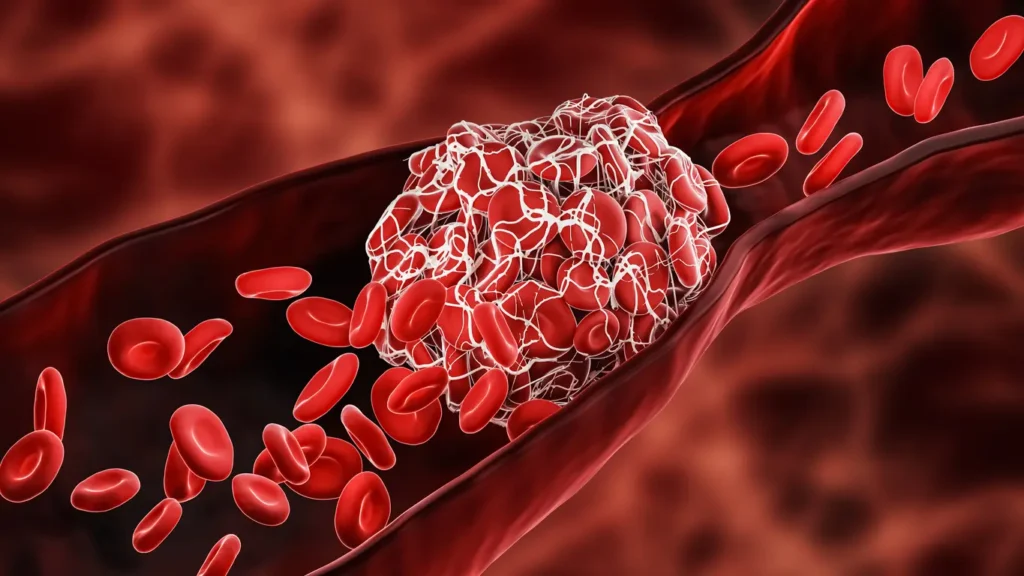
Pumps are the driving force of ECMO systems, but their interaction with blood presents inherent challenges. Advanced surface coatings offer a transformative approach to overcoming these obstacles, improving pump performance, and enhancing patient outcomes.
Smart Reactors’ Camouflage™ technology represents a significant advancement in this field, combining biomimetic design with superior hemocompatibility to redefine standards for ECMO pump coatings.
To learn more about our innovative solutions for ECMO applications, Contact us.
Share this post: on LinkedIn