For patients with end-stage renal disease (ESRD), maintaining reliable vascular access is essential for effective hemodialysis. Arteriovenous (AV) fistulas and AV grafts are among the most used long-term access options, offering stable, high-flow connections to the bloodstream. However, they remain vulnerable to complications such as thrombosis, stenosis, and infection.
This article examines the function and clinical challenges of AV access devices and explores how advanced surface coatings like Camouflage™ can help enhance their safety, longevity, and overall performance.
What Are AV Fistulas and AV Grafts?
AV Fistulas
An arteriovenous fistula is a surgically created connection between an artery and a vein, usually in the forearm or upper arm. Over time, the vein becomes thicker and stronger due to arterial pressure, enabling it to withstand repeated needle insertions during dialysis sessions.
- Gold standard for vascular access
- Lower risk of infection and clotting
- Longer maturation time (4–8 weeks)
- Ideal for long-term dialysis patients
AV Grafts
An arteriovenous graft is a synthetic tube (commonly made of expanded polytetrafluoroethylene, or ePTFE) that connects an artery to a vein. The graft serves as the site where needles are inserted to access the bloodstream during hemodialysis. It is used when the patient’s native vessels are not suitable for creating a fistula.
- Shorter maturation time (2–4 weeks)
- Higher risk of complications such as stenosis and infection
- Useful for patients with poor vein quality
Both AV fistulas and grafts are essential for dialysis, but grafts in particular benefit significantly from surface coating technologies that improve hemocompatibility and resist inflammation and infection.
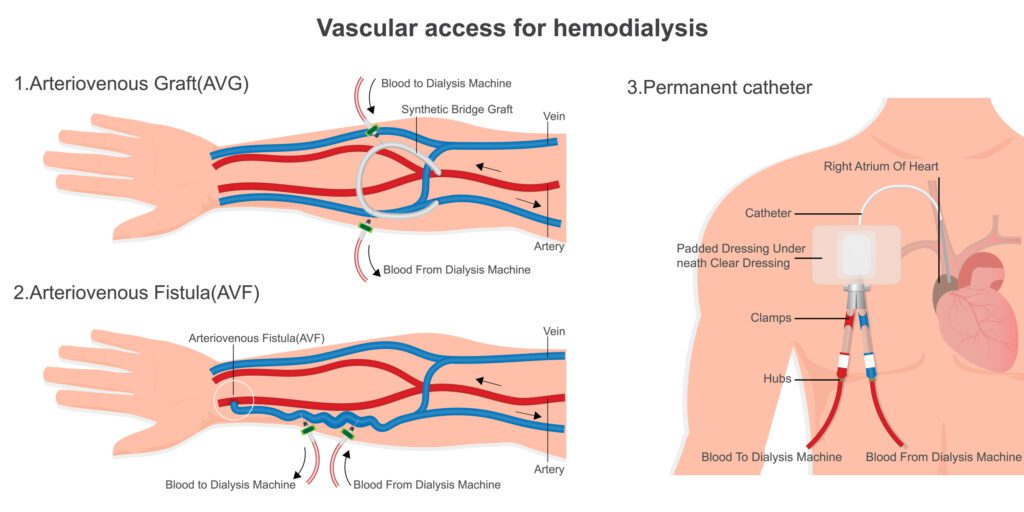
Challenges Facing AV Fistulas and Grafts
Both arteriovenous (AV) fistulas and grafts are critical for providing reliable vascular access in hemodialysis patients. However, they face significant challenges that can compromise their function and longevity:
- Thrombosis: Both fistulas and grafts are prone to clot formation, which can block blood flow and require urgent medical intervention.
- Stenosis: Narrowing of the vessels or graft material, often due to intimal hyperplasia or scarring, reduces effective blood flow and can cause access failure.
- Infection: Repeated needle punctures increase the risk of local infections, especially in synthetic grafts.
- Mechanical Wear and Damage: Grafts, being synthetic, can suffer from needle puncture damage, leading to leaks or structural weakening.
- Inflammation and Immune Response: The body’s reaction to foreign material, especially in grafts, can lead to chronic inflammation, further complicating healing and function.
While AV fistulas remodel naturally over time and have better long-term patency, they are not always feasible due to patient vessel quality. AV grafts, made from synthetic materials, offer an alternative but are more susceptible to many of these complications, limiting their durability and increasing the need for interventions.
Coating Solutions for AV Grafts
Camouflage™ coating by Smart Reactors offers a non-pharmaceutical solution specifically designed to address the challenges faced by AV grafts. By applying this advanced coating to graft surfaces, Camouflage™ coating can:
Improve Hemocompatibility : The coating inhibits clot formation on the graft surface, helping maintain consistent blood flow and reducing blockage.
Promote Controlled Endothelialization : Encouraging rapid and controlled endothelial cell growth over the graft surface helps create a more stable, durable blood-contacting layer.
Limits Inflammatory Response : Camouflage™ effectively conceals the synthetic graft material from the body’s immune system, thereby reducing inflammatory responses
Support Long-Term Function : By reducing clotting, inflammation, and surface degradation, the coating helps keep grafts functional for longer periods, reducing complications and the frequency of surgical replacements.
In summary, the fundamental roles and challenges of AV fistulas and grafts in hemodialysis vascular access have been outlined. While fistulas benefit from natural vessel remodeling, grafts face unique issues due to their synthetic nature. Camouflage™ coating presents a significant advancement in graft technology by improving biocompatibility and reducing complications. This innovation holds the potential to enhance device performance, patient safety, and long-term outcomes in dialysis care.
Share this post: on LinkedIn