Drug-eluting coatings have revolutionized neurovascular stenting, providing targeted therapeutic benefits for patients with complex cerebrovascular conditions, such as aneurysms and intracranial atherosclerotic disease (ICAD). These coatings, which release medications directly at the stent site, help address key challenges like restenosis, clot formation, and inflammation. In recent years, innovative alternatives to drug-eluting coatings, like Camouflage™, have emerged to offer comparable benefits without relying on drug delivery. Here, we explore how drug-eluting coatings and biocompatible solutions like Camouflage™ are enhancing neurovascular stenting.
The Role of Drug-Eluting Coatings in Neurovascular Stents
Neurovascular stents serve to open and support narrowed or blocked arteries in the brain. However, in neurovascular applications, complications such as restenosis, thrombosis, and inflammation pose significant risks. Drug-eluting coatings address these issues by gradually releasing therapeutic agents that prevent smooth muscle cell proliferation, reduce inflammation, and lower the risk of clot formation. By localizing drug release to the stent site, these coatings effectively target the problem area, reducing side effects and promoting a more stable recovery.
Mechanisms and Benefits of Drug-Eluting Coatings
Drug-eluting coatings consist of a layer applied to the stent surface, containing medication that releases slowly into the artery wall over time. This controlled release ensures therapeutic benefits throughout the critical stages of vessel healing and integration. The table below outlines the primary types of drug-eluting coatings and their mechanisms of action:

| Type | Purpose | Mechanism | Benefit |
| 1. Antiproliferative Drug-Eluting Coatings | To prevent restenosis by inhibiting smooth muscle cell proliferation. | Antiproliferative coatings release drugs like sirolimus or paclitaxel, which control cell growth around the stent, keeping the vessel open for proper blood flow. | Reduces the risk of restenosis.Maintains vessel patency, supporting effective blood flow. |
| 2. Antithrombotic Drug-Eluting Coatings | To prevent thrombosis by reducing the risk of clot formation on the stent surface. | Antithrombotic coatings use agents like heparin to inhibit platelet adhesion and thrombin activity, essential for minimizing ischemic risks like stroke. | Reduces thrombotic events.Enhances hemocompatibility, creating a smoother interaction between the stent and blood. |
| 3. Anti-Inflammatory Drug-Eluting Coatings | To decrease inflammation at the stent site, reducing complications. | Anti-inflammatory coatings release agents such as dexamethasone, which suppress immune reactions and lower the risk of scar tissue formation. | Lowers inflammation for better vessel healing.Encourages smoother integration with the artery wall. |
| 4. Combination Drug-Eluting Coatings | To address multiple risks by combining antiproliferative, antithrombotic, and anti-inflammatory drugs in a single coating. | Combination coatings release multiple therapeutic agents simultaneously, effectively managing the complex demands of neurovascular interventions. | Comprehensive protection from restenosis, inflammation, and clot formation.Customizable solutions based on procedural needs and patient risk profiles. |
| 5. Biodegradable Polymer-Based Drug-Eluting Coatings | To provide temporary drug delivery and eliminate long-term polymer presence. | Biodegradable coatings release drugs while breaking down gradually, leaving only the stent in place after the therapeutic effect is achieved. | Avoids long-term foreign body presence.Offers time-bound drug delivery tailored to healing phases. |
| 6. Polymer-Free Drug-Eluting Coatings | To deliver drugs directly from the stent surface without using polymers. | Polymer-free coatings utilize crystalline drug layers or micro-reservoirs that allow drug release without polymer binders, reducing inflammatory responses. | Reduces polymer-related inflammation.Enables precise, controlled drug release directly from the stent. |
Challenges and Limitations of Drug-Eluting Coatings
Despite their proven benefits, drug-eluting coatings also present several challenges and limitations, particularly in neurovascular applications. One major concern is delayed endothelisation, as the medication used to prevent excessive cell proliferation may inhibit the regrowth of endothelial cells, posing a large risk to thrombosis. Additionally, many drug-eluting coatings rely on polymer-based materials to control drug release, however, over time, these materials can provoke a localised inflammatory response within the vascular environment, potentially leading to chronic irritation and delayed healing. Furthermore, drug resistance or diminished drug efficacy in patients can reduce long-term effectiveness. These challenges highlight the need for more adaptive, biocompatible and personalized coating solutions in future stent designs.
Camouflage™: A Biocompatible Alternative to Drug-Eluting Coatings
For patients and practitioners looking for drug-free options, Camouflage™ offers an innovative biocompatible coating that delivers several benefits typically associated with drug-eluting coatings, without relying on pharmaceutical agents. Camouflage™ is a non-drug coating designed to enhance hemocompatibility, reduce thrombogenicity, and support vessel healing through endothelization.
How Camouflage™ Works:
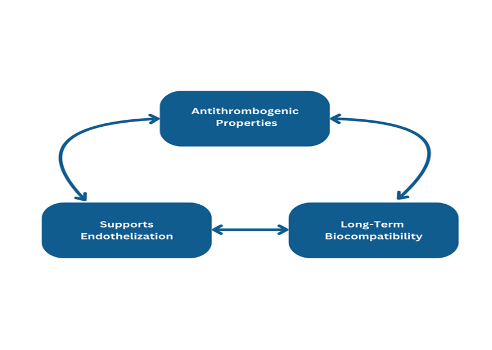
- Antithrombogenic Properties: Camouflage™ provides a blood-compatible surface that reduces platelet adhesion, lowering the risk of clot formation and thrombosis.
- Supports Endothelization: The coating promotes endothelial cell growth, creating a natural layer over the stent that integrates with the artery wall and reduces inflammation.
- Long-Term Biocompatibility: Unlike polymer-based drug-eluting coatings, Camouflage™ does not require prolonged antiplatelet therapy, making it a safer option for patients with bleeding risks.
Camouflage™ offers a compelling alternative for neurovascular stents, particularly for patients where long-term drug therapy may pose additional risks or for those seeking non-drug solutions. Its non-drug properties make it ideal for patients who may not tolerate traditional drug-eluting coatings, providing a pathway for safe, effective neurovascular stent performance.
Future Directions: Combining Drug-Eluting and Biocompatible Coatings
The continued development of both drug-eluting and biocompatible coatings promises new approaches for neurovascular stenting. With advances in nanotechnology, stent coatings will become more tailored, potentially combining drug-eluting and biocompatible features to create even more targeted solutions. . By integrating drug-eluting coatings that address immediate complications like cell proliferation and clotting with biocompatible coatings like Camouflage™ that provide a stable, long-term environment to reduce inflammation and promote vessel healing, offer comprehensive solutions. This combination has the potential to enhance the safety, effectiveness and durability of stents, ultimately leading to improved patient outcomes and a reduced risk of restenosis or thrombosis.
Conclusion: Expanding Options for Neurovascular Patients
Drug-eluting coatings have brought significant advancements to neurovascular stents, addressing key challenges like restenosis, thrombosis, and inflammation. These coatings improve stent efficacy and patient outcomes by releasing medication directly at the intervention site. However, innovations such as Camouflage™ offer an equally effective, non-drug alternative that promotes natural vessel healing and reduces the risk of complications. Together, these options allow for a more personalized approach to neurovascular stenting, providing solutions that cater to patient-specific needs.
For medical device manufacturers and healthcare providers, the availability of both drug-eluting and biocompatible coatings marks a new era in neurovascular care. As research continues, combining these technologies may offer the best of both worlds, ensuring safe, effective, and durable solutions for treating cerebrovascular conditions.
Further Reading
Biofunctional coatings and drug-coated stents for restenosis therapy – ScienceDirect
Share this post: on LinkedIn