Hemocompatible coatings are essential for reducing clot formation, preventing bacterial adhesion, minimizing inflammatory responses, and encouraging the growth of endothelial cells. These properties contribute to long-term device functionality and patient safety.
Endothelial cells form the natural lining of blood vessels. When a medical device surface supports endothelialization, it becomes more biocompatible and better integrated with the body. This is particularly crucial for implants such as stents and flow diverters, where surface compatibility directly affects performance and longevity. A coating that promotes both hemocompatibility and endothelialization represents a gold standard—Smart Reactors’ Camouflage™ coating technology achieves both.
What Makes a Coating Hemocompatible?
Key properties of a hemocompatible coating include:

- High wettability: Hydrophilic surfaces reduce blood-protein adsorption and lower the risk of triggering coagulation. Hydrophobic surfaces do the opposite—leading to thrombus formation.
- Non-toxicity: The coating must not release harmful substances into the bloodstream or damage surrounding cells.
- Durability: Coatings must remain intact throughout the device’s use. Degradation or peeling can expose thrombogenic surfaces and compromise patient safety.
- Uniformity: The coating should be evenly applied at a sub-micron thickness to maintain device performance, particularly in oxygenators and perfusion systems.
Types of Hemocompatible Coatings: Active vs. Passive
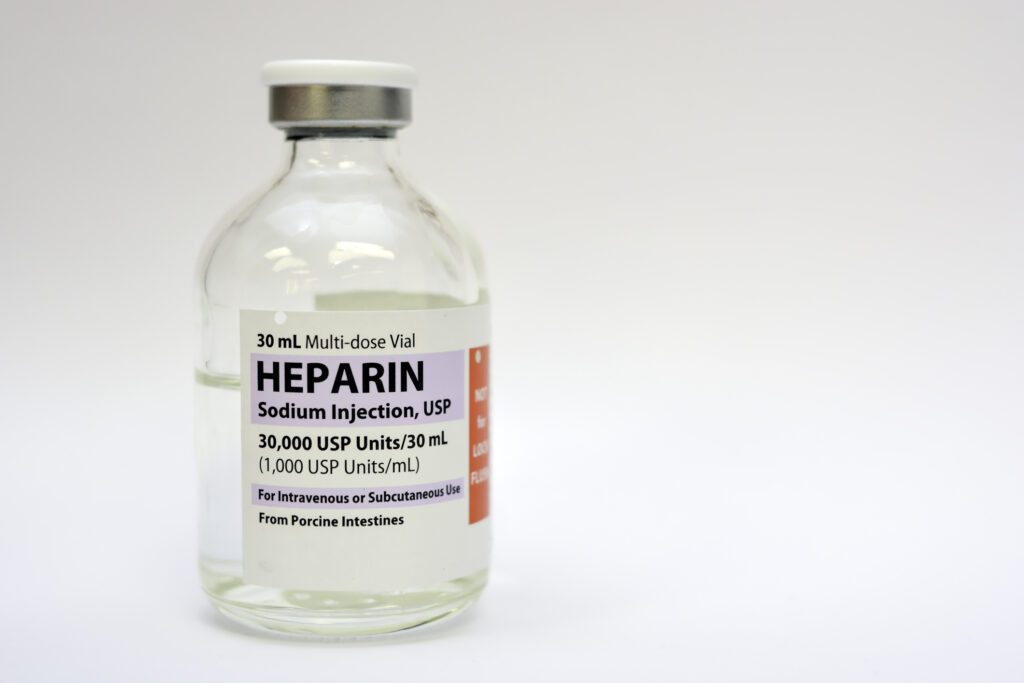
Hemocompatible coatings fall into two main categories:
Active coatings: These release or immobilize anticoagulants like heparin to prevent clot formation. While effective, they are expensive and face regulatory hurdles due to their pharmaceutical nature. Side effects, such as heparin-induced thrombocytopenia (HIT), are another concern.
Passive coatings: These minimize blood interaction without drugs. Phosphorylcholine (PC) is a common example. It mimics cell membranes and forms a hydration layer, making the device surface biologically inert. However, PC coatings don’t promote endothelialization and involve complex chemical processing.There are many different types of hemocompatible coatings on the market, all of which fall into two main categories, active or passive coatings. An active coating is one that contains a pharmaceutical anticoagulant that can be secreted into the blood or immobilized onto the device service to inhibit blood clot formation. This is compared to a passive coating which minimizes the interactions with the blood defense systems without the use of pharmaceuticals.
Smart Reactors’ Camouflage™: A Drug-Free, Passive Hemocompatible Coating
Camouflage™ Coating Technology by Smart Reactors Ltd. offers an advanced passive alternative to traditional coatings:
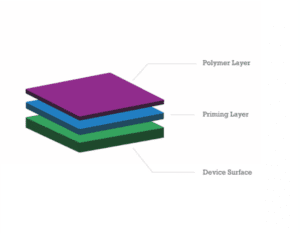
Composition: Synthetic polymer + non-inflammatory protein base
Application: Binds to nearly any substrate without surface preparation
Biocompatibility: Minimizes immune response by masking the device surface
Durability: High resilience with nanoscale thickness
Hydrophilicity: Excellent wetting properties to reduce clot formation
Fabrication: Water-based process with no harsh chemicals
Regulatory: Drug-free nature simplifies approval
Most importantly, Camouflage™ supports endothelial cell growth, setting it apart from other passive coatings.
What to Consider When Selecting a Hemocompatible Coating
Medical devices that benefit from hemocompatible coatings include:
Perfusion Equipment: Needs uniform, durable coatings to minimize clot formation during circulation.
Stents and Flow Diverters: Require both hemocompatibility and endothelialization for long-term patency.
ECMO and CPB Systems: Must maintain gas exchange—coatings should not interfere with function.
For all devices, the coating must provide:
- Enhanced hemocompatibility
- Long-lasting durability
- Uniform sub-micron application
- Support for endothelial cell growth (where applicable)
Camouflage™ checks all these boxes—and more.

Why Smart Reactors’ Camouflage™ Coating is the Future of Hemocompatible Surface Technology
Camouflage™ is gaining traction among medical device manufacturers globally for its exceptional performance and manufacturing advantages. Validated through in vitro testing, it shows no compromise in gas exchange for ECMO applications and has demonstrated robust endothelialization potential.
If you’re developing a blood-contacting medical device, Camouflage™ offers a fast-track to performance, regulatory clarity, and long-term patient safety.
Ready to upgrade your device surface? Contact Smart Reactors to explore Camouflage™ for your application.
Share this post: on LinkedIn